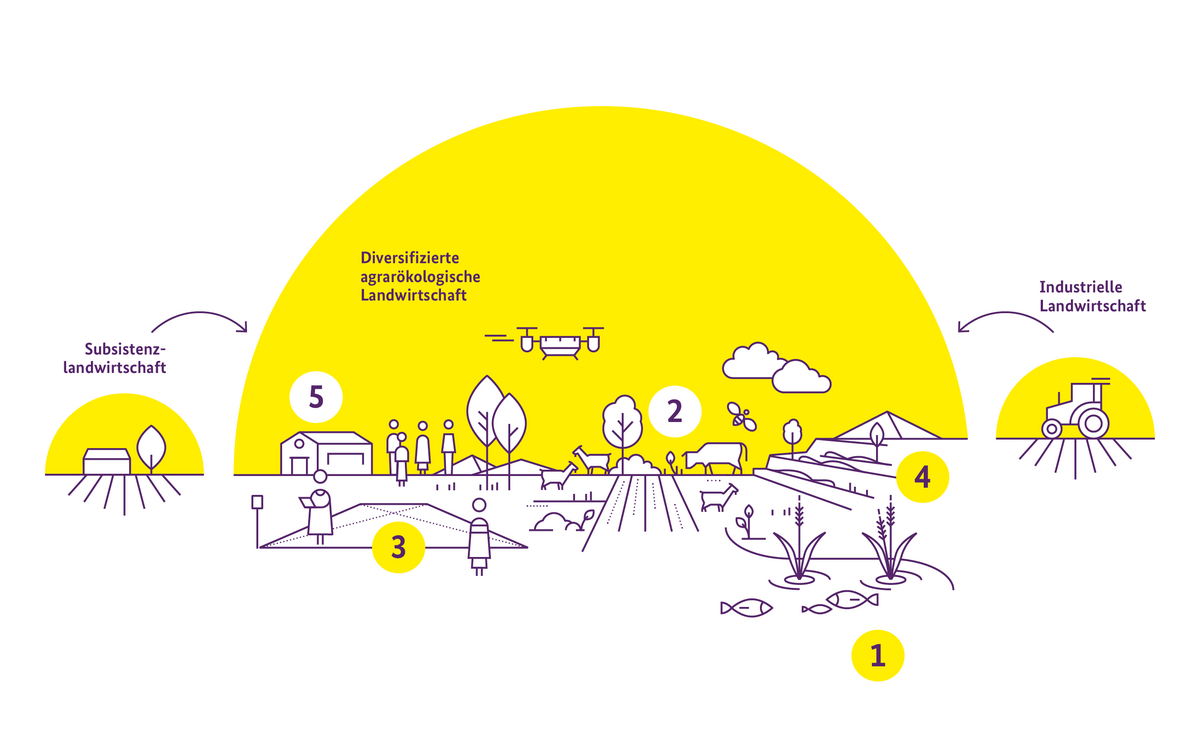
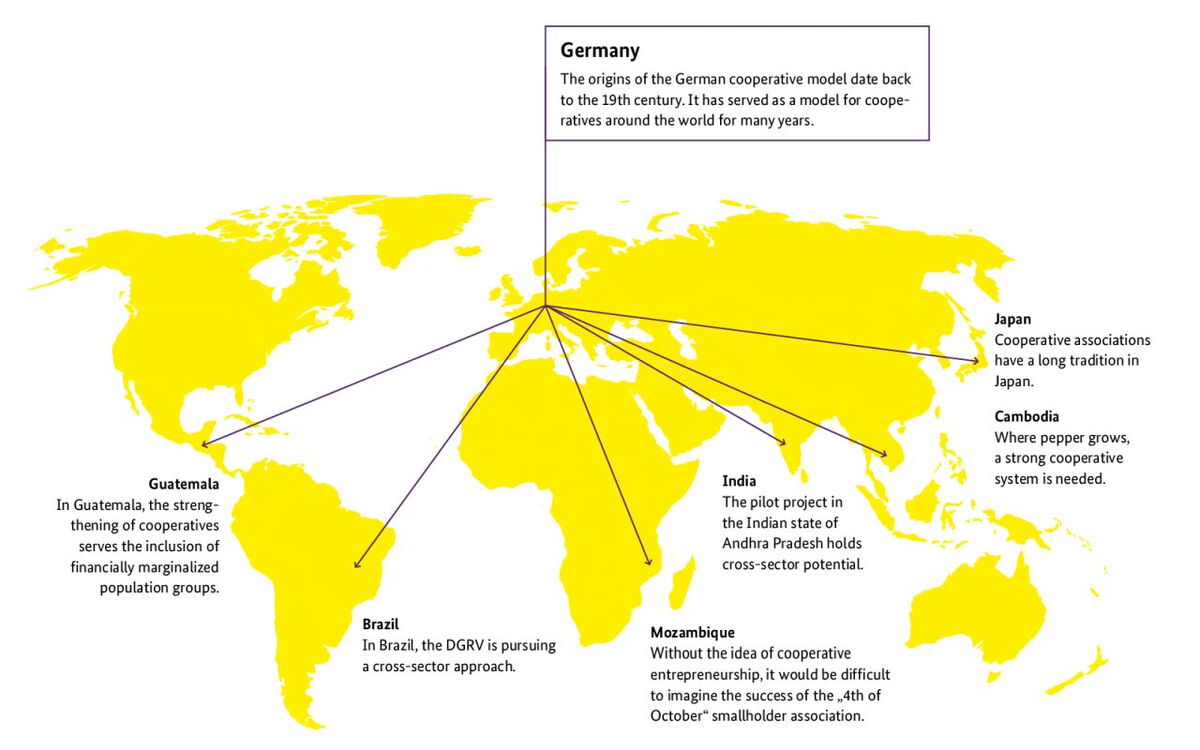
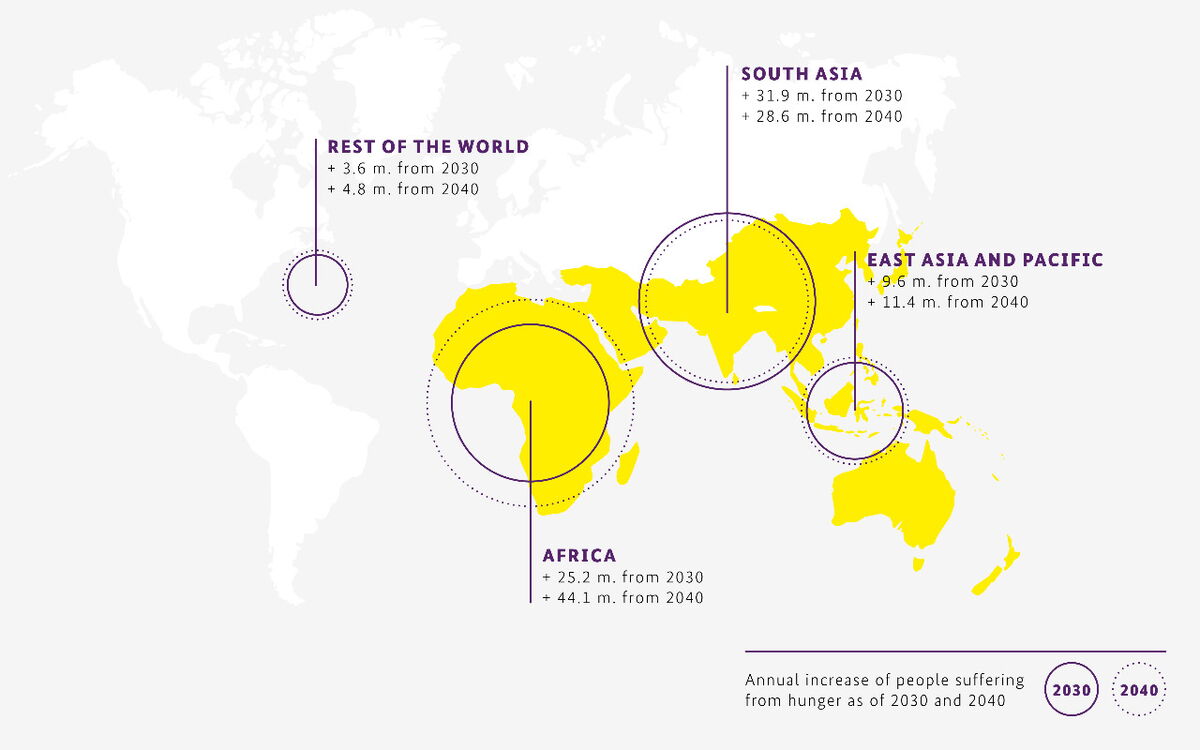
From Space to Seed: Innovation for world nutrition

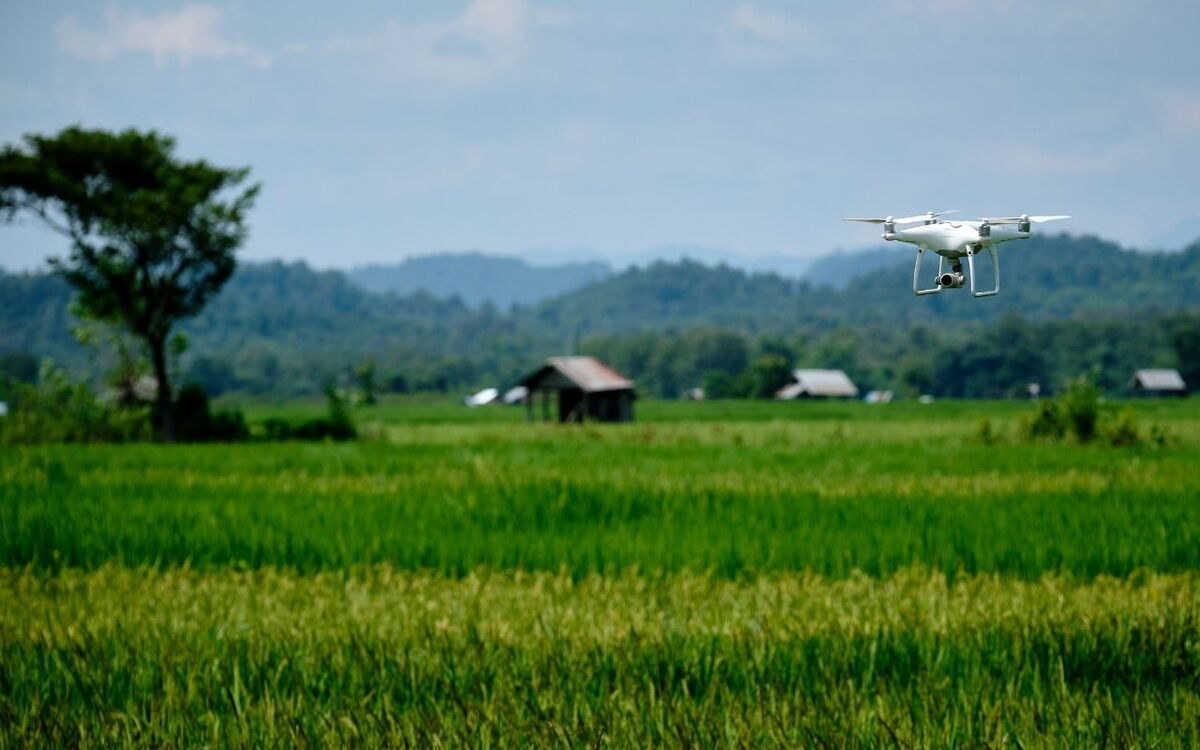
Drones and satellites:
helpful for mapping and surveying acreage, and for checking the state of vegetation and soil properties. The technologies offer farmers protection against illegal seizure of their acreage and improved accuracy of harvest forecasts. With the aid of the Sentinel-2A and -2B satellites, the chlorophyll and leaf water content of plants is recorded. This provides information on the plants’ growth and harvest forecasts from an altitude of 800 km.

Apps as toolboxes:
from animal diseases to cultivation and harvest planning, from renting agricultural equipment to building farmers’ networks. Apps offer a wide range of assistance for making agricultural work easier, more fair and more productive. In addition, apps that recognise malnutrition by means of photos or 3D scans are key tools in the fight against hunger, as they are used more often than diagnostics apps.
Cooling systems against food loss:
such as the walk-in cooling cells in Nigeria. They extend the shelf-life of foods from 2 days to 21 days and are operated sustainably with solar energy. Thanks to the invention of a cooling unit in India, farmers can use biomass and agricultural waste products to store products until market prices rise. A possibility of ecologically increasing incomes and preventing food losses estimated to cost 400 billion US dollars per year.

Silico Farming:
a calculation method that optimises plant growth. Data on real crop plants are collected, entered in a 3D model and manipulated. The models mirror real conditions so precisely that conclusions can be drawn about which factors produce plants that grow fast or are resistant to drought. The method is used primarily to prepare for possible climate change scenarios.

Aeroponics as a method of hydroponics:
plants are not grown in soil, but suspended in air. Spraying with water and nutrient solutions lets the plants grow under controlled greenhouse conditions and produces up to 100% higher growth rates than traditional agriculture. Water consumption drops by up to 90% and the plants need up to 75% less space.

Fortifier fertiliser made from faecal matter:
solves two problems at once. On the one hand, human waste is contaminating soil and water in urban areas of Ghana. On the other hand, farmers in Ghana are struggling to grow crops on nutrient-poor soils. The fertiliser is produced from faeces, minerals and food waste. It can produce 20–50% higher yields compared to conventional fertilisers without reducing soil fertility.
Crispr/Cas gene editing:
based on two components. The guide RNA, which recognises the DNA strand to be edited, and the Cas9 protein, which cuts the DNA. The process makes it possible to modify genome sequences without introducing foreign genetic material. Researchers have already successfully used the technique to develop plants that are resistant to mould, pests and drought.